Leetcode and other selected questions
Leetcode Selected Questions
(Click on ques topic to see full ques.)
Leetcode
Selected Questions
(Click on ques topic to see full ques.)
1. Split a String in Balanced Strings <Easy> : Array
|
int balancedStringSplit(string s) { int Lcount=0; int Rcount=0; int ans=0; int pointer=0; while(pointer<s.size()){ while(s[pointer]=='R'){ pointer++; Rcount++; if(Rcount==Lcount && Lcount!=0){ ans++; Lcount=0; Rcount=0; } } while(s[pointer]=='L'){ pointer++; Lcount++; if(Lcount==Rcount && Rcount!=0){ ans++; Lcount=0; Rcount=0; } } } return ans; |
=>using Stack STL : int balancedStringSplit(string s) { int count = 0; char start; stack<char> mystack; for ( char i:s ) { if ( mystack.empty() ) start = i; if ( i == start ) mystack.push(i); else mystack.pop(); if ( mystack.empty() ) count++; } return count; |
2. Check if the Sentence Is
Pangram <Easy> :Array
bool checkIfPangram(string sentence) {
unordered_map<char,int> uMap;
for (int i = 0; i < sentence.size(); ++i)
{
uMap[sentence[i]]++; // key is Alphabet, ++ increase its frequency
}
if(uMap.size()==26) return true;
else return false;
}
3. Greatest Common Divisor
of Strings<Easy>:Array
string gcdOfStrings(string str1, string str2) {
string ans="";
if(str1+str2!=str2+str1) return ans;
ans+=str1.substr(0,__gcd(str1.size(),str2.size()));
// __gcd(,) is c++ inBuilt method to find gcd
return ans;
}
4. Lemonade Change
<Easy>:Array
bool lemonadeChange(vector<int>& bills) {
int c5=0,c10=0;
for(int i=0;i<bills.size();i++){
if(bills[i]==5) c5++;
else if(bills[i]==10){
c10++;c5--;
}
else if(bills[i]==20){
if(c10>0){
c10--;c5--;
}
else c5-=3;
}
if(c5<0) return false;
}
return true;
}
5. Relative Ranks <Easy>:Array
vector<string> findRelativeRanks(vector<int>& score) {
// int max=*max_element(score.begin(),score.end());
vector<string> v;
map<int, int> mp;
for(auto &i:score) mp[i]=1;
int i=score.size();
//by default map sorted in ascending order A/C to its key
for(auto &it:mp) it.second=i--;
// for(auto &it:mp) cout<<it.first<<" "<<it.second<<endl;
vector<string> ans;
for(auto &scoreValue:score){
switch(mp[scoreValue]){
case 1: ans.push_back("Gold Medal"); break;
case 2: ans.push_back("Silver Medal"); break;
case 3: ans.push_back("Bronze Medal"); break;
default : ans.push_back(to_string(mp[scoreValue]));
}
}
return ans;
}
Wilson’s
theorem, in number
theory, theorem that any prime p divides (p − 1)! + 1, where n! is the factorial notation for 1 × 2 × 3 × 4 × ⋯ × n. For example, 5 divides (5 − 1)! + 1 = 4! + 1 =
25.
***************************************************************************
Count the number of prime numbers less than a non-negative number,n.
Sieve of
Eratosthenes
youtube linkwebsite link in map c++, Attention:
suppose map is: map<char,int> mp;
iteration start to end:
M1:
for (auto it :mp){
cout << it.first << " = " << it.second<<endl;
}M2: for (auto it = mp.begin();it != mp.end(); it++){
cout << it->first << " = " << it->second<<endl;
}
note: second ko -- krne ke liye it.second-- ya it->second-- n use krke mp[it.second]-- ya mp[it->second]-- hi use kro
conclusion: M1 me '.' work kiya jbki M2 me '->' so carefull
reverse iteration:
for(auto it=mp.rbegin();it!=mp.rend();it++){
cout << it->first << " = " << it->second<<endl;
}ek aur baat jb hum auto nhi use krte tb 'it' declaration ke liye :
::reverse_iterator it;
access first pair: mp.begin()->first and mp.begin()->second6. Increasing Decreasing String :hashmap
string sortString(string s) { map<char, int> mp; for(auto ch:s) mp[ch]++;
string res="";while(res.size()!=s.size()){ for (auto it :mp){ if(it.second>0){ res.push_back(it.first); mp[it.first]--; } } for(auto it=mp.rbegin();it!=mp.rend();it++){ if(it->second>0){ res.push_back(it->first); mp[it->first]--; } } } return res; }
check key exist in map or not
if ( m.find(key) == m.end() ) not found;
else found;
7. Destination City: hashmap
8.Isomorphic Strings: hashmap
8.Contains Duplicate II:hashMap
9.Word Pattern: hashMap
Ascii Values
- For capital alphabets 65 – 90
- For small alphabets 97 – 122
- For digits 48 – 57
char to Ascii value: e.g. int(a) =>97,
int('0') =>48,
int('5') =>> 53,
but num char to int ke liye: e.g. '5'-'0' =>5
number string to integer:
atoi("42") is 42
atoi("3.14159") is 3
atoi("31337 geek") is 31337 stoi("45") is 45 stoi("3.14159") is 3 stoi("31337 geek") is 31337atoi() is a legacy C-style function. stoi() is added in C++ 11.
note:stoi(), atoi() is for string num
for char num , can use above method: '5'-'0' => 5
or first convert char to string as : string s;
s+='5' => now s is "5"
hence stoi(s)=> stoi("5") => 5
for large integer string , stoi overflow:
check type in c++:
#include <typeinfo>
...
cout << typeid(variable).name() << endl;
9. Number of Different Integers in a String
10.X of a Kind in a Deck of Cards:hashMap
11.Range Sum of BST:Binary tree
11.Merge Two Binary Trees:Binary Tree
12.Increasing Order Search Tree: Binary Tree
void inorder( vector<TreeNode*> &v, TreeNode* root){ // as a helper function if(root!=NULL){ inorder(v,root->left); v.push_back(root); inorder(v,root->right); } } TreeNode* increasingBST(TreeNode* root) { vector<TreeNode*> v; inorder(v,root); for(int i=0;i<v.size()-1;i++){ v[i]->left=NULL; v[i]->right=v[i+1]; } v[v.size()-1]->left=NULL; v[v.size()-1]->right=NULL; return v[0]; }13. Search in a Binary Search Tree:Binary Tree
TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) { if(!root) return NULL; if(root->val==val) return root; if(val <root->val) return searchBST(root->left, val); if(val> root->val) return searchBST(root->right,val); //in last, since non void-finction like in int main return 0 , here is return NULL return NULL; }14.Sum of Root To Leaf Binary Numbers:Binary Tree
int total_sum=0; void dfs(TreeNode* root,int curr_sum){ if(!root) return; curr_sum=curr_sum*2+root->val;
if(!root->left && !root->right) { total_sum+=curr_sum; return; } dfs(root->left,curr_sum); dfs(root->right,curr_sum); } int sumRootToLeaf(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return 0; dfs(root,0); return total_sum; }15. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
vector<int> v; void dfs(TreeNode*root,int depth){ if(!root) return; depth++; if(!root->left && !root->right){ v.push_back(depth); depth=0; } dfs(root->left,depth); dfs(root->right,depth); } int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return 0; dfs(root,0); return *max_element(v.begin(),v.end()); }
OR
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return 0; int left_height=maxDepth(root->left); int right_height=maxDepth(root->right); return 1+max(left_height,right_height); }16.Invert Binary Tree
17.Univalued Binary Tree
18.Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
OR
vector<int> res;
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if(root != NULL){
inorderTraversal(root->left);
res.push_back(root->val);
inorderTraversal(root->right);
}
return res;
}
19.Average of Levels in Binary Tree
vector<double> v; vector<double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode* root) { queue<TreeNode*> q; q.push(root); while(!q.empty()){ int n=q.size(); // size of q double sum=0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ TreeNode* frontNode=q.front(); sum+=frontNode->val; q.pop(); if(frontNode->left) q.push(frontNode->left); // if left child add to queue if(frontNode->right) q.push(frontNode->right); // if right child add to queue } double avg=sum/n; v.push_back(avg); } return v; }
20. Leaf-Similar Trees:Binary Tree
void dfs(TreeNode*root, vector<int> &v){ // base case if(!root) return; // formulae , push back val if it is leaf node if(!root->left && !root->right) v.push_back(root->val); // recursion,for left and right subtree dfs(root->left,v); dfs(root->right,v); } bool leafSimilar(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) { vector<int> v1,v2; dfs(root1,v1); dfs(root2,v2); if(v1.size()!=v2.size()) return false; int n=v1.size(); for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if(v1[i]!=v2[i]) return false; } return true; }21. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
TreeNode* convertToBST(vector<int>&nums,int l,int r){ // base case if(l>r) return NULL; int mid=(l+r)/2; TreeNode* root=new TreeNode(); root->val=nums[mid]; root->left= convertToBST(nums,l,mid-1); root->right=convertToBST(nums,mid+1,r); return root; } TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) { TreeNode* root=convertToBST(nums,0,nums.size()-1); return root; }22.Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
vector<int> v; void dfs(TreeNode* root){ // base case if(!root) return; // recursion,for left and right subtree then formulae since post order if(root->left) dfs(root->left); if(root->right) dfs(root->right); // formulae v.push_back(root->val); } vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { dfs(root); return v; }23.Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
vector<int> v; void dfs(TreeNode* root){ // base case if(!root) return; // since preorder, hence first formulae then recursion for left and right subtree v.push_back(root->val); if(root->left) dfs(root->left); if(root->right) dfs(root->right); } vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { dfs(root); return v; }convert num to string : to_string(num)
24.Binary Tree Paths
vector<string> v; void dfs(TreeNode* root,string s){ if(!root) return; s+=to_string(root->val); // leaf node if(!root->left && !root->right) v.push_back(s); // other wise else{ s+="->"; dfs(root->left,s); dfs(root->right,s); } } vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) { dfs(root,""); return v; }
minimal abs difference between any two elements of vector:
sort(v.begin(),v.end());
int min=v[1]-v[0];
for(int i=2;i<v.size();i++){
if(v[i]-v[i-1] <min) min=v[i]-v[i-1];
}
return min;
25.Minimum Absolute Difference in BST
vector<int> v; void dfs(TreeNode* root){ if(!root) return ; v.push_back(root->val); dfs(root->left); dfs(root->right); } int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) { dfs(root); sort(v.begin(),v.end()); int min=v[1]-v[0]; for(int i=2;i<v.size();i++){ if(v[i]-v[i-1] <min) min=v[i]-v[i-1]; } return min; }
check two vector are same or not : return(v1==v2)
26.Same Tree: Binary Tree
false
27: Path Sum : Binary Tree
Acess second key of map:
mp.erase(mp.begin());
auto it=mp.begin();
return it->first; or
int count=0;
int second_min;
for(auto it:mp){
if(count==1){
second_min=it.first;
break;
}
count++;
}
return second_min;28. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
kthSmaalest in arr: less time without using map
Input:
N = 5
A[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Output:
5 1 2 3 4Kadane's Algorithm: Largest sum contiguous Subarray
convert string to lower or uppercase:
remember : all lowercase letter > all uppercase letter
capitalize any char in string : s[i]=toupper(s[i])
built in to reverse string:
Check if two strings are permutation of each other
newNode creation in LinkedList: important
using structure:struct Node{ int data; struct Node* next;};
struct Node *newNode(int key){ struct Node *temp =(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); temp->data = key; temp->next = NULL; return temp;}
int main(){ struct Node *head = newNode(1);
return 0;}simple to add node at front:
Node *newwNode=newNode(7);
newwNode->next=head; head=newwNode;but attention when using via func to add node at front since refrence conceptvoid addToFront(Node** head_ref, Node* newwNode){ newwNode->next=*head_ref; *head_ref=newwNode;}in main: Node *newwNode=newNode(7); addToFront(&head,newwNode);insert newwNode After given node :
void insertAfterGivenNode(Node* givenNode,Node* newwNode){ if(!givenNode) return; -givenNode- -givenNode ke baad ka node newwNode->next=givenNode->next; ^ givenNode->next=newwNode; newwNode}in main: insertAfterGivenNode(givenNode,newwNode);
insert newwNode at End node :
void insertAtEnd(Node** head_ref,Node* newwNode){ if(!*head_ref){ newwNode=*head_ref; return; }
Node* tmp=*head_ref; // tmp ko head par pahunchaya while(tmp->next){ tmp=tmp->next; } // ab jb tmp last node pr pahunch gya tmp->next=newwNode;}in main: insertAtEnd(&head,newwNode);deleteNodeForGivenKey : first occurence key node
void deleteNodeForGivenKey(Node** head_ref,int key){ // first ocuurence key Node* tmp=*head_ref;
// agar head pr hi key mil gyi to if(tmp && tmp->data==key){ // head ko age phunchakar, delete phla head *head_ref=tmp->next; delete tmp; return; }
// tmp ke saath ek prev node chalana padega Node *prev=NULL; while(tmp && tmp->data!=key){ prev=tmp; tmp=tmp->next; } // if key is not present if(!tmp) cout<<"key not present";return;
// jb tmp us key wale node pr pahunch gya prev->next=tmp->next; delete tmp;
}in main: deleteNodeForGivenKey(&head,7);count total node: recursively
delete node at given position:
void deleteNodeAtPosition(Node** head_ref,int pos){ // pos like index here if(!head_ref) return; Node *tmp=*head_ref; // if position is 0 if(pos==0){ *head_ref=tmp->next; delete tmp; return; } if(pos> countNode(*head_ref)-1){ cout<<"invalid postion"; return; }
Node* prev=NULL; for(int i=0;i!=pos;i++){ prev=tmp; tmp=tmp->next; }
// ab jb tmp us pos pr pahunch gya prev->next=tmp->next; delete tmp; return;
}in main:deleteNodeAtPosition(&head,2);delete whole linked list:
void deleteWholeList(Node** head_ref){
Node* current=*head_ref; Node* next=NULL; // next to cuurnet ke next pahunchate jana aur current to delete krte jaana while(current){ next=current->next; delete current; current=next; } //deref head_ref to affect the real head back in the caller
*head_ref=NULL;}in main: deleteWholeList(&head);search ele position if present: recursive
int pos=0;void searchElement(Node* head,int key){ if(!head) { cout<<"not found"; return; } if(head->data==key){ cout<<"found at : "<<pos; return; } pos++; searchElement(head->next,key);}in main: searchElement(head,4);get data at given index:
int getGivenIndexData(Node* node,int index){ if(!node) return -1; // out of range index
if(index==0) return node->data; index--; return getGivenIndexData(node->next,index);}in main: getGivenIndexData(head,2)Reverse a linked list:
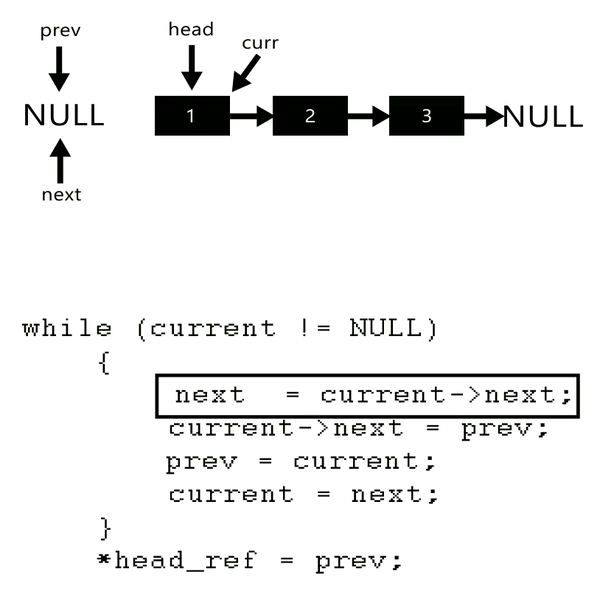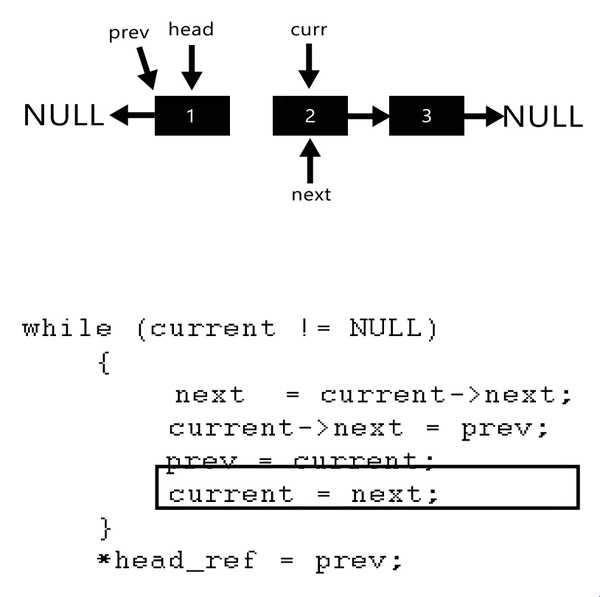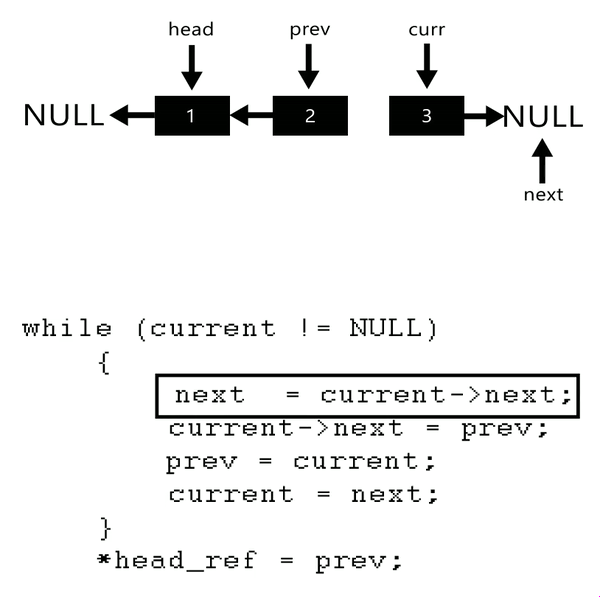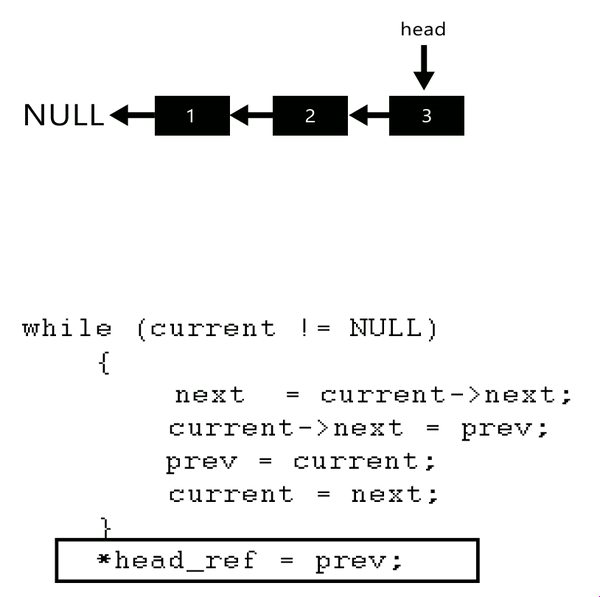
Input: Head of following linked list
1->2->3->4->NULL
Output: Linked list should be changed to,
4->3->2->1->NULLInput: Head of following linked list
1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Output: Linked list should be changed to,
5->4->3->2->1->NULL
here see gif to understand better
void reverseList(Node** head_ref){Node* prev=NULL;Node* current=*head_ref;Node* next=NULL;//approach:// 1. next ko current ke next pr pahunchaya => prev current next// 2. current ke next ko prev se add => prev<-current next// 3. prev ko current pr pahunchaya// 4. current ko next pr pahunchaya => current ek kadam aage khiskawhile(current){next=current->next;current->next=prev;prev=current;current=next;}// jb current nhi hoga tb prev last node pr pahunch chuka hoga// isliye prev ko hi head bna diya*head_ref=prev;}in main:reverseList(&head);
store res of string : recurision
for same recursion order:vector<string> v;void storeRos(string s){ // base case if(s.length()==0) return; string ros=s.substr(1); v.push_back(s); storeRos(ros); }
accces last char of string:
remove duplicates from string
input : geeksforgeeks
output: geksfor
Output: geksfor
input : caaabbbaacdddd
output: cabd
remove All adjacent duplicates from string
Input: azxxzy
Output: ay
First “azxxzy” is reduced to “azzy”.
The string “azzy” contains duplicates,
so it is further reduced to “ay”.
Input: geeksforgeeg
Output: gksfor
First “geeksforgeeg” is reduced to
“gksforgg”. The string “gksforgg”
contains duplicates, so it is further
reduced to “gksfor”.
Input: caaabbbaacdddd
Output: Empty String
Input: acaaabbbacdddd
Output: acac
following code are in exception:
int main(){ string s; cin>>s; stack<char> st; string ans=""; for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){ if(st.empty()){ st.push(s[i]); continue; } if(st.top()==s[i]) st.pop(); else st.push(s[i]); }
while(!st.empty()){ ans=st.top()+ans; st.pop(); } cout<<ans; return 0;}
take sentence input
string s; getline(cin,s);level order binary tree
..............pointer with array
sort 2D arr row wise:using double pointer
update 2D array: single pointer
29.Minimum Add to Make Parentheses Valid
reverse string:recursion
power of 2:recursion
int threeKiPower(int n){ if(n==0) return 1; if(n==1) return 3;
if(n%2==0) return threeKiPower(n/2)*threeKiPower(n/2); else return threeKiPower((n+1)/2)*threeKiPower(n/2);}
int main() { int n; cin>>n;
cout<<threeKiPower(n);
return 0; }
base ki power n: recursion
check arr is sorted or not:recursion
bool isSorted(int* arr,int i,int sz){ // base case 2 if(i>=sz) return true; //also work for single ele arr since sz 1 //ek baat ka dhyan rakhna, jo hmari last recursion tk ki cond hogi use phle likhna // islye base case2 phle likha hai
// base case 1 if(arr[i-1]>arr[i]) return false;
return isSorted(arr,i+1,sz);}
int main() { int arr1[5]={1,4,6,8,7};
cout<<isSorted(arr1,1,5)<<endl;
int arr2[8]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
cout<<isSorted(arr2,1,8)<<endl; int arr3[1]={2}; cout<<isSorted(arr3,1,1);
return 0; }-----------






























Comments
Post a Comment